XML
The XML datasource allows you to display data from an XML source in Smartsign.
This makes it possible to integrate data from external systems, APIs, or internally published XML files into your digital signage content.
XML (Extensible Markup Language) is a structured data format commonly
used to exchange information between systems.
It organizes data in a hierarchical structure, which makes it possible
to extract and display individual values on screens.

This datasource is intended for users with basic technical knowledge of
XML and XPath.
While powerful, it may be more complex to configure compared to other
datasources.
How it works
When connected, Smartsign retrieves XML data from the specified source URL and makes it available in the Template Creator using XPath expressions.
The XML data can be fetched either:
- Via the Smartsign server (default, cached for performance and security).
- Directly from the source by the screen or player, depending on your configuration.
The retrieved data can then be databound to text or other elements in a template.
Requirements
To use the XML datasource, you need:
- An accessible XML source available over HTTP or HTTPS.
- The XML source must be encoded in UTF-8
- Basic technical knowledge of XML and XPath for configuring data bindings.
If you plan to use direct requests, the XML source must also support browser-based access and comply with standard CORS rules.
Set up the datasource
The first step is to configure your data source with the XML source you want to use.
In this example we will use a basic URL without any request headers or requirements, but you can read more about them in the configuration details below.
The URL should look like something like this: https://server.example.com/data.xml
- Go to Template datasources and select create new datasource.
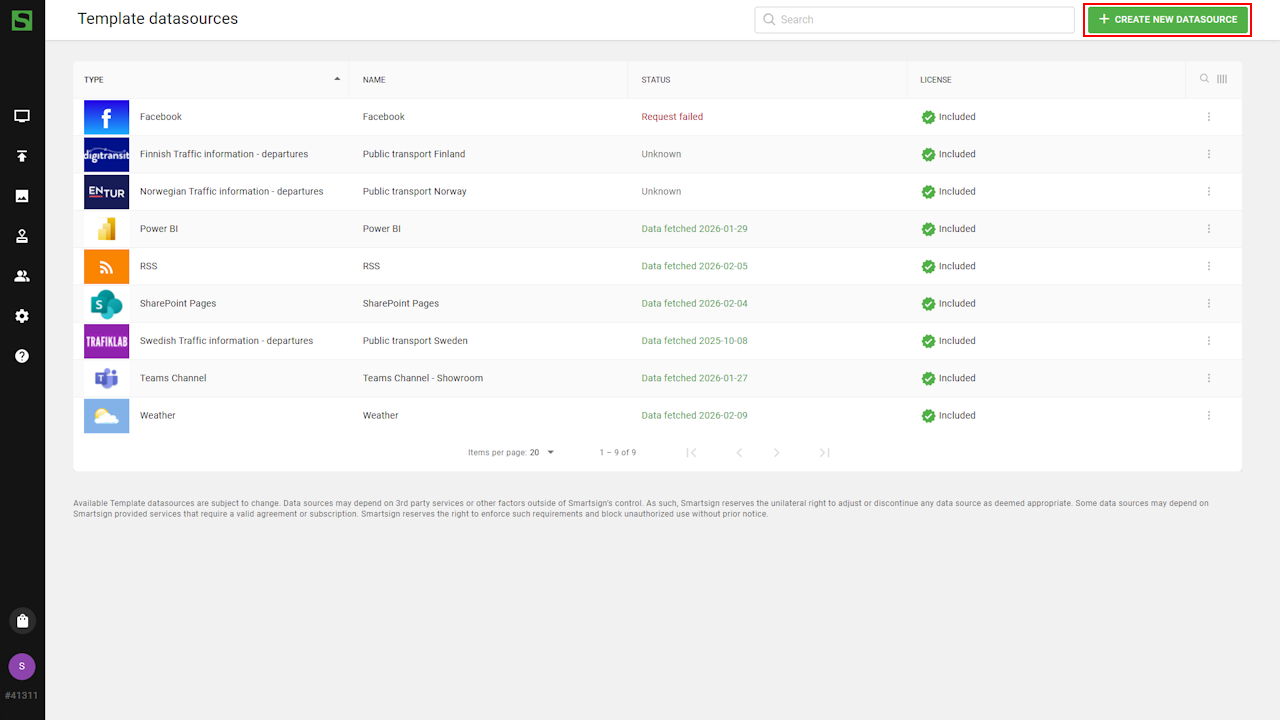
- Select the XML datasource.
- Configure the datasource by adding Name, Description
and XML Link.
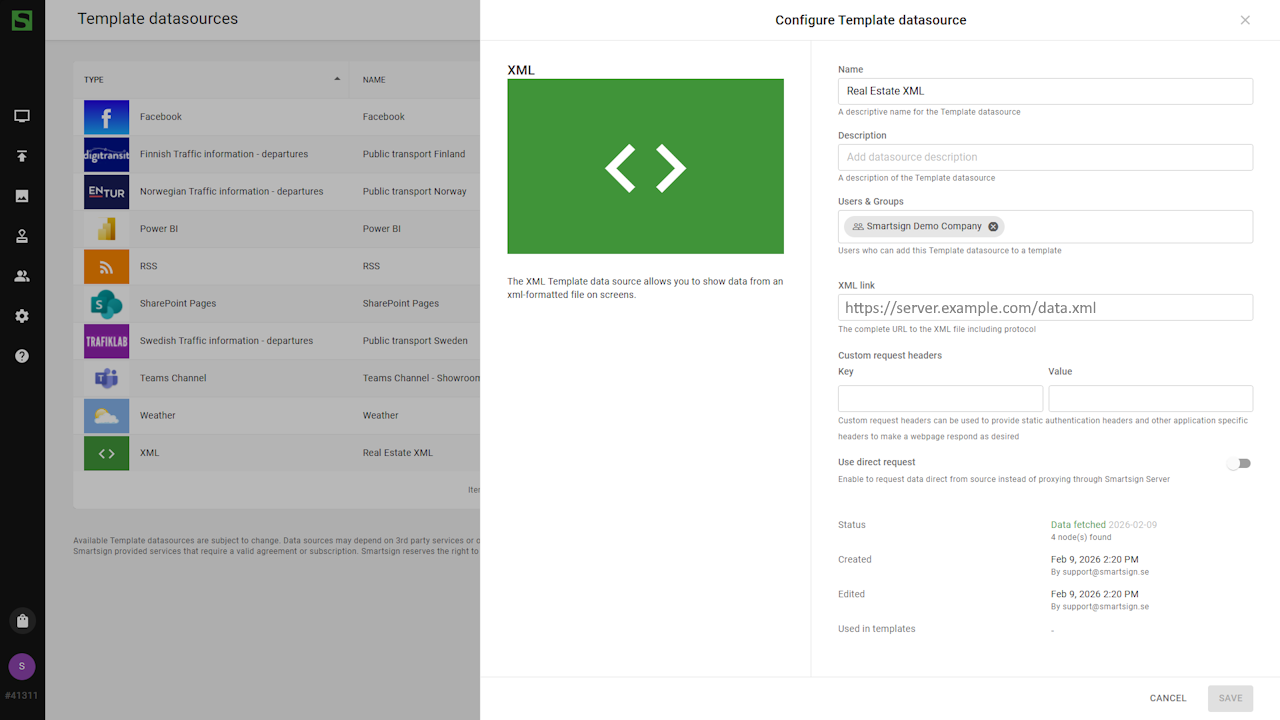
- Click Create and verify data connection to see if data can be fetched.
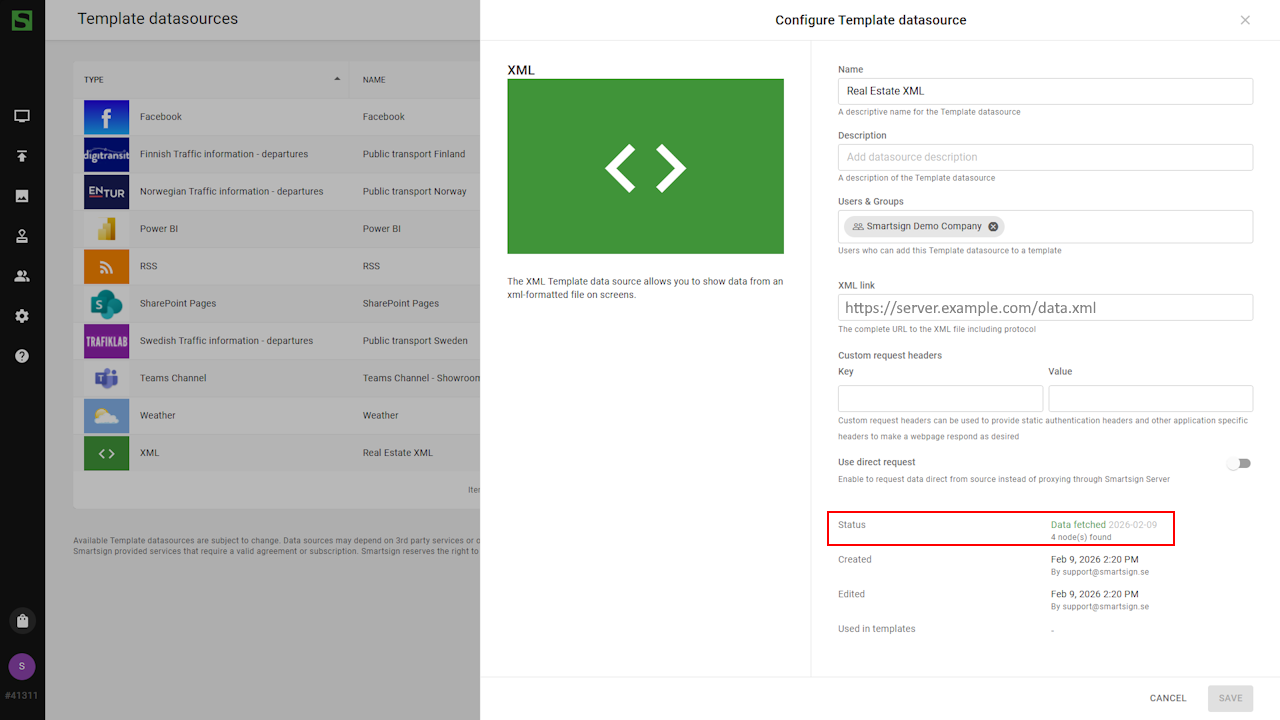
- Once created, you can confirm that data has been fetched.
Datasource is now ready to be used.
Identifying XPath expressions
Before creating the template, you need to identify the XPath expressions required to fetch data for each field.
XPath is used to tell Smartsign where in the XML structure a specific value is located. An XPath expression describes the path from the root of the XML document to the element you want to display.
Each level in the XML hierarchy is separated by a /.
Example structure
<root>
<ads>
<estate>
<price>€ 989,000</price>
<street>176 Hillview Sidings St.</street>
<property-type>Single family residence</property-type>
</estate>
</ads>
</root>
How to find the Xpath
- Start at the root element. In this case, the root element is
<root>. - Follow the structure down to the value you want. Each nested element becomes part of the path.
- End with the element containing the value.
root/ads/estate/pricewill result in € 989,000
Xpath examples
| Field | Xpath | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Street address | /root/ads/estate/street | 176 Hillview Sidings St. |
| Price | /root/ads/estate/price | € 989,000 |
| Property type | /root/ads/estate/property-type | Single family residence |
| Description | /root/ads/estate/description | Property description text |
| Image | /root/ads/images/url | Image URL |
Common tips
- XPath is case-sensitive
- Element names must match exactly as they appear in the XML
- If your XML contains namespaces, enabling Remove namespace definitions can simplify XPath usage
- Start simple and bind one field first and verify the output before adding more
Create an XML template
An XML template can either be created from scratch, or you can download a suitable template from the Marketplace and adapt it to your needs. If you are new to templates, please see the Template Creator guide to learn the basics.
-
Create or download templates from the Templates menu.
-
Open the template and add text fields and image placeholders for the Xpath data.
-
Bind each element to its corresponding XPath expression.
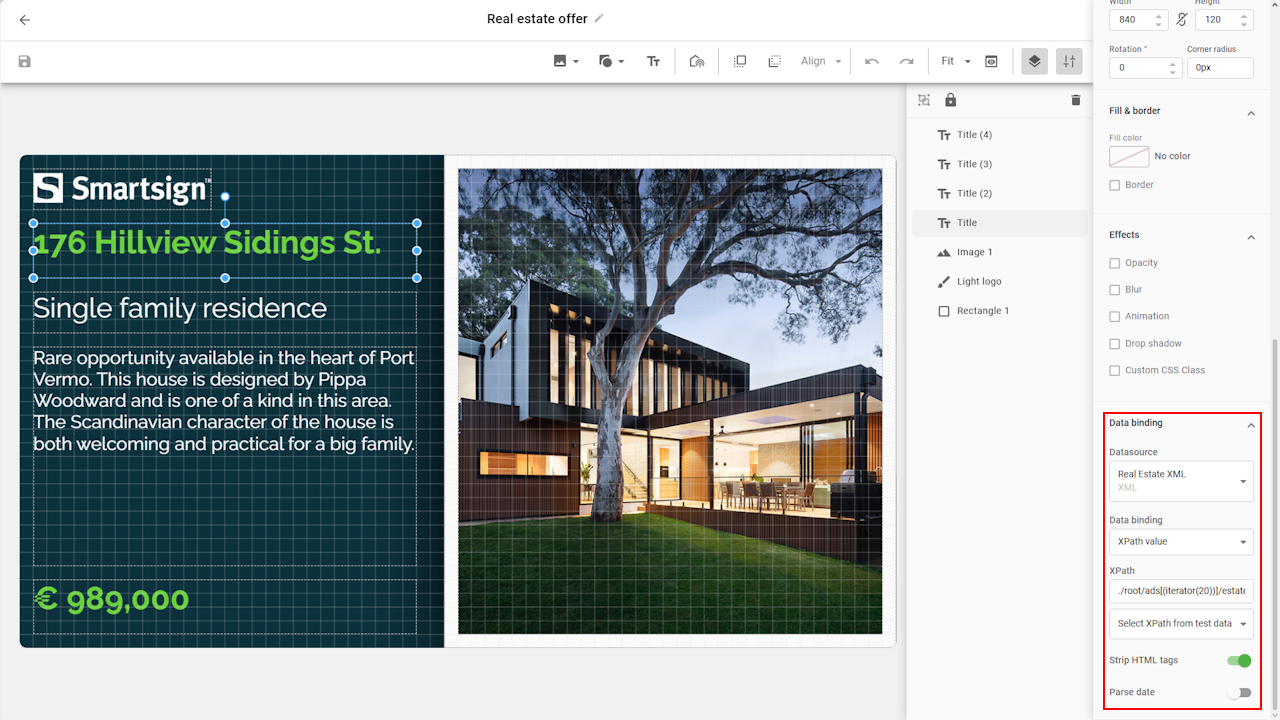 The Select XPath from test data option helps you identify the correct
XPath when binding fields.
The Select XPath from test data option helps you identify the correct
XPath when binding fields.- Street Address
./root/ads[(iterator(20))]/estate/street - Property type
./root/ads[(iterator(20))]/estate/property-type - Description
./root/ads[(iterator(20))]/estate/description - Price
./root/ads[(iterator(20))]/estate/price - Image
./root/ads[(iterator(20))]/images[(iterator(20))]/url
- Street Address
What is the iterator?
The iterator is used when your XML feed contains multiple items and you want to display them one at a time.
In the examples above, the value 20 specifies how many seconds each item
is shown before switching to the next.
It is important that all XPath expressions use the same iterator value
to keep the content in sync.
If you want to display a single object or select a specific item from a list, you can use an index instead.
./root/ads[0]/estate/street selects the first item from the list.
Technical information
XML source must be encoded in UTF-8
XML datasource configuration options
|
Setting |
Description |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
XML Link |
The full URL to the XML source, including protocol (HTTP/HTTPS). |
https://server.example.com/data.xml |
|
Data Update Time |
Time in seconds between updates Restrictions (regardless of set value) |
3600 |
| Iterator interval |
Defines how long (in seconds) each item in a multi-item XML feed is shown
before switching to the next. This value must match the iterator value used in all XPath expressions to keep content synchronized. |
20 |
|
Special request headers |
HTTP header key and value pairs |
Key =
Authorization |
| Use direct requests |
Enable to request data direct from source instead of proxying through Smartsign Server Server fetched data is cached by the server for 10 minutes for load balancing and security. Direct fetched data is subject to browser security rules |
False |
| Remove namespace definitions | Enable to
automatically remove any xml namespaces included in the data. This may help if you have trouble getting data from your Xpaths. |
True |